手把手原生js简单轮播图
在团队带人,突然被人问到轮播图如何实现,进入前端领域有一年多了,但很久没自己写过,一直是用大牛写的插件,今天就写个简单的适合入门者学习的小教程。当然,轮播图的实现原理与设计模式有很多种,我这里讲的是用面向过程函数式编程去实现,相对于面向对象设计模式,代码难免会显得臃肿冗余。但没有面向对象的抽象却很适合新手理解与学习。已经在BAT的同学看到希望少喷点。另外可以多提意见。
轮播图的原理:
一系列的大小相等的图片平铺,利用CSS布局只显示一张图片,其余隐藏。通过计算偏移量利用定时器实现自动播放,或通过手动点击事件切换图片。
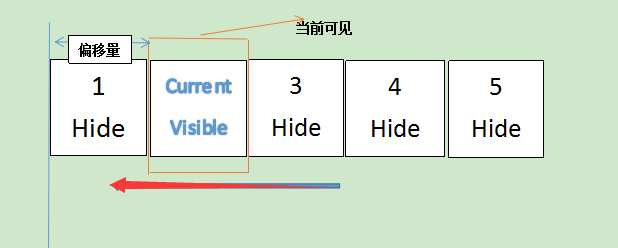
Html布局
首先父容器container存放所有内容,子容器list存在图片。子容器buttons存放按钮小圆点。
<div id="container">
<div id="list" style="left: -600px">
<img src="img/5.jpg" alt="1" />
<img src="img/1.jpg" alt="1" />
<img src="img/2.jpg" alt="2" />
<img src="img/3.jpg" alt="3" />
<img src="img/4.jpg" alt="4" />
<img src="img/5.jpg" alt="5" />
<img src="img/1.jpg" alt="5" />
</div>
<div id="buttons">
<span index="1" class="on"></span>
<span index="2"></span>
<span index="3"></span>
<span index="4"></span>
<span index="5"></span>
</div>
<a href="javascript:;" id="prev" class="arrow"><</a>
<a href="javascript:;" id="next" class="arrow">></a>
</div>
优化,无缝滚动。
当你从最后一张图切换回第一张图时,有很大空白,利用两张辅助图来填补这个空白。
这里补充下无缝滚动,直接看代码,复制最后一张图片放置第一张图片前,同时复制第一张图片放置最后一张图片的后面。并且,将第一张图片辅助图(实际上是实际显示的第5张图片隐藏起来,故设置style="left: -600px;")
CSS修饰
1、对盒子模型,文档流的理解,绝对定位问题。
2、注意list的overflow:hidden;只显示窗口的一张图片,把左右两边的都隐藏起来。
3、确保buttons中每个span所在层置顶,将其设置为最顶端。(z-index:999)我这里设置为z-index:2
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
text-decoration: none;
}
body {
padding: 20px;
}
#container {
position: relative;
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
border: 3px solid #333;
overflow: hidden;
}
#list {
position: absolute;
z-index: 1;
width: 4200px;
height: 400px;
}
#list img {
float: left;
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
}
#buttons {
position: absolute;
left: 250px;
bottom: 20px;
z-index: 2;
height: 10px;
width: 100px;
}
#buttons span {
float: left;
margin-right: 5px;
width: 10px;
height: 10px;
border: 1px solid #fff;
border-radius: 50%;
background: #333;
cursor: pointer;
}
#buttons .on {
background: orangered;
}
.arrow {
position: absolute;
top: 180px;
z-index: 2;
display: none;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
font-size: 36px;
font-weight: bold;
line-height: 39px;
text-align: center;
color: #fff;
background-color: RGBA(0, 0, 0, .3);
cursor: pointer;
}
.arrow:hover {
background-color: RGBA(0, 0, 0, .7);
}
#container:hover .arrow {
display: block;
}
#prev {
left: 20px;
}
#next {
right: 20px;
}
Js
首先我们先实现出手动点击左右两个箭头切换图片的效果:
window.onload = function () {
var list = document.getElementById("list");
var prev = document.getElementById("prev");
var next = document.getElementById("next");
function animate(offset) {
//获取的是style.left,是相对左边获取距离,所以第一张图后style.left都为负值,
//且style.left获取的是字符串,需要用parseInt()取整转化为数字。
var newLeft = parseInt(list.style.left) + offset;
list.style.left = newLeft + "px";
}
prev.onclick = function () {
animate(600);
};
next.onclick = function () {
animate(-600);
};
};
运行后我们会发现,一直点击右箭头 ,会出现空白,而且,不能回到第一张图片。要点击左箭头才能回到第一张图片。
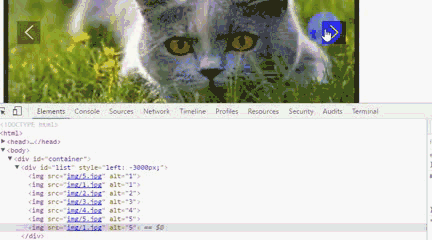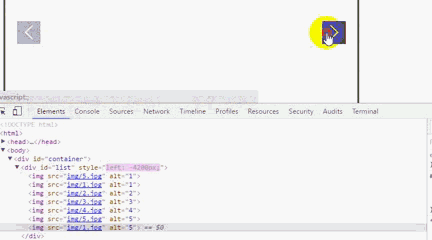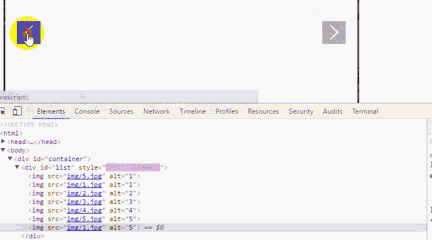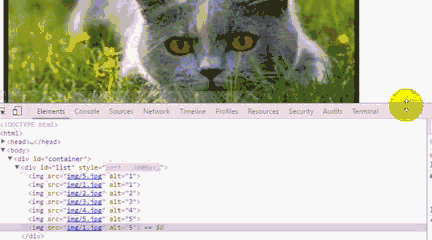
利用谷歌浏览器F12,原因是我们利用偏移量left来获取图片,当看到left值小于3600时,因为没有第8张图片就出现空白,所以这里我们需要对偏移量做一个判断。
在animate函数里加上这么一段:
if (newLeft < -3000) {
list.style.left = -600 + "px";
}
if (newLeft > -600) {
list.style.left = -3000 + "px";
}
好,运行一下,没问题了。轮播图,顾名思义,是自己会动的图片,这个时候我们需要用到浏览器的内置对象定时器。
对于定时器,有必要说明一下setInterval()跟setTimeout的区别了。简单来说,setInterval()执行多次,setTimeout()只执行一次。
更具体的用法可以点击链接查看区别:window.setInterval window.setTimeout 。
这里我们是用setInterval(),因为我们的图片需要循环滚动。插入下面
var timer;
function play() {
timer = setInterval(function () {
prev.onclick();
}, 1500);
}
play();
运行,ok!
但是,当我们想仔细看某一张图片时候,要把图片停住,我们清楚定时器就可以了,这里用到window.clearInterval 这个方法。
这里,我们需要对其DOM操作,需要获取整个轮播图区域;
var container = document.getElementById("container");
function stop() {
clearInterval(timer);
}
container.onmouseover = stop;
container.onmouseout = play;
但这里,一个轮播图基本算完成了,有同学·会问,那么简单。看到图片下面的那一排小圆点没。我给你加功能了。
这里是升级版:
var buttons = document.getElementById("buttons").getElementsByTagName("span");
var index = 1;
function buttonsShow() {
//这里需要清除之前的样式
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
if (buttons[i].className == "on") {
buttons[i].className = "";
}
}
//数组从0开始,故index需要-1
buttons[index - 1].className = "on";
}
prev.onclick = function () {
index -= 1;
if (index < 1) {
index = 5;
}
buttonsShow();
animate(600);
};
next.onclick = function () {
//由于上边定时器的作用,index会一直递增下去,我们只有5个小圆点,所以需要做出判断
index += 1;
if (index > 5) {
index = 1;
}
buttonsShow();
animate(-600);
};

现在看起来正常多了吧,但我们想实现通过鼠标任意点击其中一个小圆点,切换到相应的图片,原理同样,我们还是需要通过偏移量去找到对应的图片。
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
buttons[i].onclick = function () {
// 在浏览器的控制台打印一下,看看结果
console.log(i);
/* 偏移量获取:这里获得鼠标移动到小圆点的位置,用this把index绑定到对象buttons[i]上,去谷歌this的用法 */
/* 由于这里的index是自定义属性,需要用到getAttribute()这个DOM2级方法,去获取自定义index的属性*/
var clickIndex = parseInt(this.getAttribute("index"));
var offset = 600 * (index - clickIndex);
animate(offset); //存放鼠标点击后的位置,用于小圆点的正常显示
index = clickIndex;
buttonsShow();
};
}
到这一步时,以为大功告成?你在控制台会发现打印出来的永远的是i=5。
错误原因:没有正确获取i值,使用闭包就可以了。你在高级程序设计第三版中76页,会看到这么一句话:
“对javascript来说,由for语句创建的变量i即使在for循环执行结束后,也依旧会存在于循环外部的执行环境中。”
就是说,js没有块级作用域这东西,(可能我C写多了,混淆了)。在第一次循环(从 i=0 到 4 这一过程)结束后,最后的 i 获取到的为 buttons.length 的值被
保存在for循环之外,最后鼠标点击任何一个小圆点时,自然访问的一直是 i=5 了。
正确代码如下:
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
// 这里使用的是立即执行函数,
(function (i) {
buttons[i].onclick = function () {
var clickIndex = parseInt(this.getAttribute("index"));
var offset = 600 * (index - clickIndex);
animate(offset);
index = clickIndex;
buttonsShow();
};
})(i);
}
有关闭包的知识我不展开来说,要说的又一大推,
大家可以参考下我很久之前的博客: 头疼的闭包 https://www.cnblogs.com/LIUYANZUO/p/5074194.html

大家,可能发现了,这个轮播图有点奇怪,不中规中矩,它是向左切换的,改写一下:
function play() {
//将轮播图换成向右切换图片
timer = setInterval(function () {
next.onclick();
}, 2000);
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
text-decoration: none;
}
body {
padding: 20px;
}
#container {
position: relative;
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
border: 3px solid #333;
overflow: hidden;
}
#list {
position: absolute;
z-index: 1;
width: 4200px;
height: 400px;
}
#list img {
float: left;
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
}
#buttons {
position: absolute;
left: 250px;
bottom: 20px;
z-index: 2;
height: 10px;
width: 100px;
}
#buttons span {
float: left;
margin-right: 5px;
width: 10px;
height: 10px;
border: 1px solid #fff;
border-radius: 50%;
background: #333;
cursor: pointer;
}
#buttons .on {
background: orangered;
}
.arrow {
position: absolute;
top: 180px;
z-index: 2;
display: none;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
font-size: 36px;
font-weight: bold;
line-height: 39px;
text-align: center;
color: #fff;
background-color: RGBA(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
cursor: pointer;
}
.arrow:hover {
background-color: RGBA(0, 0, 0, 0.7);
}
#container:hover .arrow {
display: block;
}
#prev {
left: 20px;
}
#next {
right: 20px;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
/* 知识点: */
/* this用法 */
/* DOM事件 */
/* 定时器 */
window.onload = function () {
var container = document.getElementById("container");
var list = document.getElementById("list");
var buttons = document
.getElementById("buttons")
.getElementsByTagName("span");
var prev = document.getElementById("prev");
var next = document.getElementById("next");
var index = 1;
var timer;
function animate(offset) {
//获取的是style.left,是相对左边获取距离,所以第一张图后style.left都为负值,
//且style.left获取的是字符串,需要用parseInt()取整转化为数字。
var newLeft = parseInt(list.style.left) + offset;
list.style.left = newLeft + "px";
//无限滚动判断
if (newLeft > -600) {
list.style.left = -3000 + "px";
}
if (newLeft < -3000) {
list.style.left = -600 + "px";
}
}
function play() {
//重复执行的定时器
timer = setInterval(function () {
next.onclick();
}, 2000);
}
function stop() {
clearInterval(timer);
}
function buttonsShow() {
//将之前的小圆点的样式清除
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
if (buttons[i].className == "on") {
buttons[i].className = "";
}
}
//数组从0开始,故index需要-1
buttons[index - 1].className = "on";
}
prev.onclick = function () {
index -= 1;
if (index < 1) {
index = 5;
}
buttonsShow();
animate(600);
};
next.onclick = function () {
//由于上边定时器的作用,index会一直递增下去,我们只有5个小圆点,所以需要做出判断
index += 1;
if (index > 5) {
index = 1;
}
animate(-600);
buttonsShow();
};
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
(function (i) {
buttons[i].onclick = function () {
/* 这里获得鼠标移动到小圆点的位置,用this把index绑定到对象buttons[i]上,去谷歌this的用法 */
/* 由于这里的index是自定义属性,需要用到getAttribute()这个DOM2级方法,去获取自定义index的属性*/
var clickIndex = parseInt(this.getAttribute("index"));
var offset = 600 * (index - clickIndex); //这个index是当前图片停留时的index
animate(offset);
index = clickIndex; //存放鼠标点击后的位置,用于小圆点的正常显示
buttonsShow();
};
})(i);
}
container.onmouseover = stop;
container.onmouseout = play;
play();
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="container">
<div id="list" style="left: -600px">
<img src="" alt="1" />
<img src="" alt="1" />
<img src="" alt="2" />
<img src="" alt="3" />
<img src="" alt="4" />
<img src="" alt="5" />
<img src="" alt="5" />
</div>
<div id="buttons">
<span index="1" class="on"></span>
<span index="2"></span>
<span index="3"></span>
<span index="4"></span>
<span index="5"></span>
</div>
<a href="javascript:;" id="prev" class="arrow"><</a>
<a href="javascript:;" id="next" class="arrow">></a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
这里结合评论,补充下:
就算是初学者也要特别注意代码规范问题,上面的CSS实在太不规范了,难怪我带的人都不怎样,哈哈哈。。。
Css的书写顺序
CSS里最好不用或直接不用id来改变样式(我这里是id为了方便DOM操作)
这里推荐css规范的技术文章
前端前辈的博客: http://www.cnblogs.com/hustskyking/p/css-spec.html
或者这位大神的Github:https://github.com/fex-team/styleguide/blob/master/css.md
以及KISSY v1.4 Documentation的css编码规范: http://docs.kissyui.com/1.4/docs/html/tutorials/style-guide/css-coding-style.html
over
最后,我们完成了一个简单的轮播图,在我的 Github 里可以找到源码。觉得不错就star一下。